Abstract
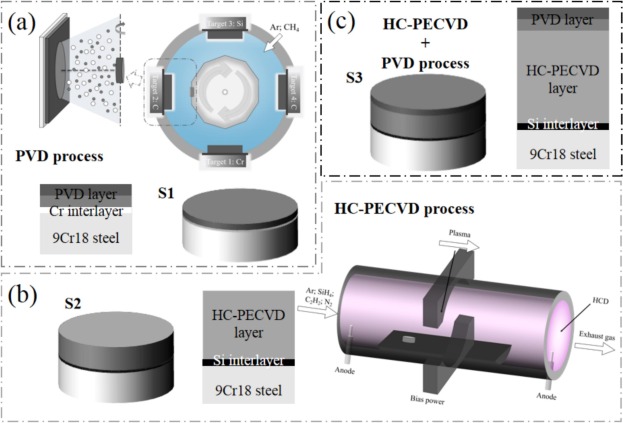
Three hydrogenated amorphous carbon (a-C:H) coatings were prepared by physical vapor deposition (PVD), hollow cathode plasma chemical vapor deposition (HC-PECVD) and PVD combined HC-PECVD co-deposition technique. The effects of different deposition techniques on the structural, mechanical, tribological and corrosion properties of the coatings were systematically investigated. The results show that the co-deposited Si/a-C:H:Si:N/ a-C:H:Si coating prepared by co-deposition achieved the coverage of surface defects through the deposition of the top layer, and the higher ductility of the top layer also promoted the adhesive properties of the coating. The codeposited coating exhibited excellent wear and abrasion resistance, with a wear rate of 2.93 x 10- 7 mm3/Nm in a 20 h long-life dry friction test, which represented a 40 % reduction compared to the HC-PECVD coating. And the wear rate in the 10 h tribocorrosion test was 9.29 x 10- 8 mm3/Nm, showing a 17 % decrease relative to the PVD coating. In terms of corrosion resistance, by virtue of the dense structure of the a-C:H:Si top layer and the thickness advantage of the a-C:H:Si:N sublayer, the corrosion current density of the co-deposited coatings was as low as 2.40 x 10-10 A/cm2, which is an order of magnitude lower than that of the a-C:H coatings prepared by the two single deposition techniques. In summary, the combination of the PVD and HC-PECVD techniques enabled the successful preparation of a-C:H coating with long life, as well as outstanding wear and corrosion resistance.
Keywords Plus:DIAMOND-LIKE CARBON,TRIBOLOGICAL PERFORMANCE,MECHANICAL-PROPERTIES,FILMS,BEHAVIOR,MICROSTRUCTURE
Published in SURFACE & COATINGS TECHNOLOGY,Volume513;10.1016/j.surfcoat.2025.132450,OCT 1 2025


