Abstract
Against the backdrop of global energy and environmental crises, the technology of CO2 hydrogenation to produce methanol is garnering widespread attention as an innovative carbon capture and utilization solution. Bimetallic oxide catalysts have emerged as the most promising research subject in the field due to their exceptional catalytic performance and stability. The performance of bimetallic oxide catalysts is influenced by multiple factors, including the selection of carrier materials, the addition of promoters, and the synthesis process. Different types of bimetallic oxide catalysts exhibit significant differences in microstructure, surface active sites, and electronic structure, which directly determine the yield and selectivity of methanol. Although bimetallic oxide catalysts offer significant advantages over traditional copper-based catalysts, they still encounter challenges related to activity and cost. In order to enhance catalyst performance, future investigations must delve into microstructure control, surface modification, and reaction kinetics. (c) 2025, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
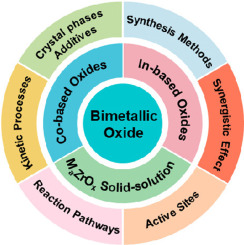
Keywords Plus:SELECTIVE HYDROGENATION,CU/ZRO2 CATALYSTS,OXYGEN VACANCY,ADSORPTION,PERFORMANCE,SURFACE,COBALT,CARBON,REDUCTION,INSIGHTS
Published in CHINESE JOURNAL OF CATALYSIS,Volume73;10.1016/S1872-2067(25)64689-4,JUN 2025


