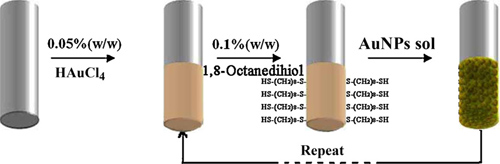
Schematic diagram of Au NPs/SPME fiber preparation process.
Researchers of the CAS Key Laboratory of Chemistry of Northwestern Plant Resources, Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics (LICP), have prepared a novel solid-phase microextraction fiber based on a stainless steel wire coated with Au nanoparticles using a simple layer by layer self-assembly method.
Coupled with gas chromatography (GC) analysis, the fiber exhibits fine extraction efficiency and selectivity. The established Au NPs/SPME-GC method has been used to extract several aromatic hydrophobic organic chemicals (HOCs) pollutants in aqueous solutions, which achieved a wide linearity ranges and low limits of detection (LODs). The method was then applied to two real natural samples; four analytes were detected and quantified.
The novel Au NPs/SPME fiber showed high stability and durability towards acid, alkali and under high temperature. Both the single fiber repeatability and fiber-to-fiber reproducibility were satisfactory. Au NPs can be a good sorbent for SPME.
Au NPs have been widely used in capillary electrochromatography and capillary electrophoresis. Currently available utilization in the sample preconcentration is mainly focused on solid-phase extraction, nanoparticle-single drop microextraction and solid-phase nanoextraction. However, extraordinary properties of Au NPs deserve further investigations in other sample preparation method such as in SPME.
Based on these considerations, researchers prepared the novel Au NPs/SPME fiber which has remarkable selectivity towards compounds with high hydrophobicity and large π-electron systems.
The work ahs received support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, National Science & Technology Major Project of China and Technology R&D Program of Gansu Province of China.
The findings have been published in Journal of Chromatography A (Journal of Chromatography A, 1217 (2010) 8079–8086).


