A novel Pd-catalyzed direct and selective C3-acetoxylation of indole derivatives has been accomplished by researchers of Wuhan University and Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics of the CAS.
This selective CH activation reaction was implemented without the assistance of directing groups and took place under mild conditions. The kinetic study revealed that the reaction was zero-order with respect to the oxidant and first-order with respect to the indole derivatives.
Direct functionalization of C-H bonds has been a hot topic in organic chemistry during recent years. Arenes—one of the most abundant chemical motifs—usually have multiple C-H bonds. Although, some examples of direct functionalizations of arenes have been reported recently, the selectivity of C-H bond activation remains a challenge(Scheme 1 A). Several strategies have been applied to achieve selective C-H activation; these mainly included orthodirecting groups or selective deprotonation–metallation.
By employing the directing-group strategy (Scheme 1 B), direct acetoxylation of arene C-H bonds has received considerable attention during the past few years. Even for traditional C-O cross-coupling reactions that employ ArX as the electrophile, efficient examples are rare.
The detailed report has been published in Chem. Eur. J. (Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 2353 – 2357).
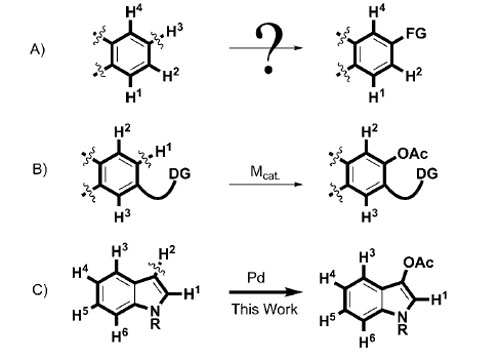
Selectivities of direct C-H functionalizations of arenes: A) without and B) with a directing group as well as C) the approach used herein. FG=functional group; DG=directing group; the wavy lines highlight the chemical bonds involved in C-H activation process and represent the neglected structures in the molecules.


