Supercapacitors, one of the most promising electrochemical energy storage systems, have attracted more and more attention due to their pulse power supply, long cycle life, and high dynamic of charge propagation. Up to now, much work has been devoted to the graphene-based composites for supercapacitor applications. However, it should be noted that most of the working electrodes in the literatures were binder-enriched electrodes. The binder will decrease the electrical conductivity of electrode materials, hindering the potential application in high performance supercapacitors. Therefore, to obtain the ideal electrochemical performance it is very important to develop novel, flexible and binder-free electrode materials for supercapacitors.
Researchers at the State Key Laboratory of Solid Lubrication of the Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics have synthesized free-standing, flexible, and binder-free graphene/manganese dioxide (MnO2) composite papers (GMCP) by thermal reduction of graphene oxide/MnO2 composite paper (GOMCP) and evaluated their structural characteristics and electrochemical properties for potential application in supercapacitors.
The electrochemical tests in the 0.1 M Na2SO4 aqueous solution revealed a good capacitive behavior in a potential window of 0–0.8 V vs. Ag/AgCl. The maximum specific capacitance of 256 Fg-1 was achieved at a discharge current density of 500mAg-1 for GMCP-24. The flexible and binder-free nature, plus good electrochemical performance make GMCP a promising electrode material for supercapacitors.
The findings have been published in J. Mater. Chem. (J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21, 14706–14711).
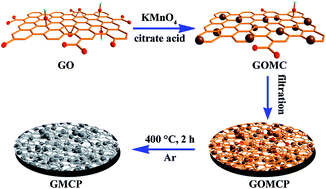
A schematic illustration of the fabrication processes of the GMCP.


