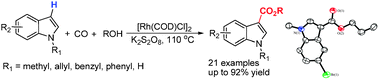Researchers at the State Key Laboratory for Oxo Synthesis and Selective oxidation of the Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics and Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics have developed a Rh-catalyzed reaction protocol for the direct carbonylation of indoles to form indole-3-carboxylates.
This [Rh(COD)Cl]2/K2S2O8 catalyst system showed high regioselectivity and good substance tolerance under mild conditions. These features demonstrated by current methodology also point out a way forward to develop direct carbonylations of heteroarenes with other partners.
Triflates and tosylates with CO and alcohol have became one of the most straightforward access to carboxylic esters which are important structural motifs in many valuable commodity chemicals and fine chemicals. Recently, aromatic C–H functionalizations have found increasing applications in the preparation of organic building blocks and therapeutically important scaffolds due to the advantage of avoiding the prefunctionalization of Ar–H and thereby the usage of a stoichiometric amount of bases. However, efficient and regioselective synthesis of carboxylic ester through direct C–H bond oxidative carbonylation of nonchelating substance is still a challenging area.
The work has received support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Chinese Academy of Sciences. The findings have been published in Chem. Commun. (Chem. Commun., 2011, 47, 12553–12555).