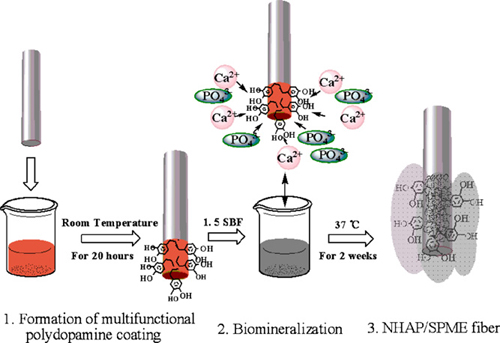
Schema of preparation procedures of the fiber.
A novel nanostructured hydroxyapatite (NHAP)/solid-phase microextraction (SPME) fiber has been prepared by a simple polydopamine-assisted biomineralization process by researchers from Key Laboratory of Chemistry of Northwestern Plant Resources of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Extraction performance was evaluated by extracting several polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in aqueous samples. Analytical parameters were all investigated, which demonstrated the fine extraction capabilities of the fiber. According to the distribution of PAHs in environment matrix, both aqueous and solid samples were used to test the reliability of the SPME–GC method.
Partition coefficients of the analytes between the coating and the aqueous solution were estimated and correlated with their Log Ps. Extraction mechanism was suggested based on the experimental results and some related references, which predicted its potential extraction capability to other compounds with large π- electron system.
Due to the fine compatibility with metal substrates and the multifunctional property for surface modification, polydopamine has sparked great interest as binding agent in the preparation of SPME fiber with metal wire as support.
SPME has got considerable developments and wide analytical applications since its first introduction. To overcome the fragile drawback of the fused-silica fiber, metal wires become promising support substrates for SPME. However, because of the chemically inert property, modification of the metal wire is difficult and complicated, which brings much limitation for its application. In recent years, some special processes have been introduced to prepare metal-based SPME fibers. Most of the methods mentioned above were innovative and practical, but cannot be applied to many other absorbents because of their selectivity and specificity towards the support and absorbent materials.
The robust dopamine-derived films (polydopamine) contains catechol and quinine functional groups, and can subsequently support a variety of secondary reactions to create a wide range of functional surfaces So preparation of SPME coatings on stainless steel wire can be developed via polydopamine derivation with organic or inorganic absorbent materials.
The work has received support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The findings have been published in Journal of Chromatography A (Journal of Chromatography A, 1218 (2011) 3601–3607).


