The Ni-catalyzed α-arylation of nitriles by using readily prepared α-bromonitriles and arylboronic acids or esters which are being widely used in synthetic chemistry have been reported by researchers from the Wuhan University and Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics for the first time. The use of Ni(acac)2 and PPh3 as the catalyst precursor has a significant practical advantage over the reported methods.
The α-aryl substituted nitrile moieties are very important constituents in many medicinal and natural products. With their impressive bioactivities, they are extensively used as synthetic intermediates in the pharmaceutical industry. However, only limited methods for the synthesis of α-aryl nitriles have been reported until recently. In these cases, the aryl group all acted as an electrophile (Fig. 1, Path I). Normally, a strong base has to be employed for the deprotonation of nitriles to form the active
However, from the disconnection of the designed products a-aryl nitriles, an alternative approach also has high potentials, in which aryl groups are used as nucleophiles, such as aryl triflorosilanes, aryl boronic acids and aryl zinc reagents. From the nature of these two approaches, the advantages of the second one are very obvious. The reaction conditions are milder. Strong bases are avoided in the deprotonation of the nitriles, hence the functional groups tolerance is highly improved. However, very few results have been reported by this protocol.
The work has received support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Program on Key Basic Research Project of China (973 Program), “the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities”, and Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET).
The findings have been published in Org. Biomol. Chem. (Org. Biomol. Chem., 2011, 9, 5343–5345).
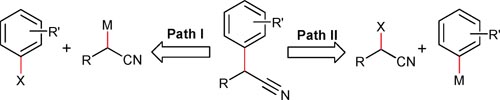
Two possible approaches to obtain a-aryl nitriles.


