Abstract: A new BODIPY-based derivative 1 bearing phenolic OH groups was developed as a fluorescent sensor for Cu(II) ions and homocysteine/cysteine. Receptor 1 behaves as an “on–off” fluorescent sensor for the selective and sensitive detection of Cu(II) ions. The mechanism for the fluorescence response of receptor 1 toward Cu(II) ions could be explained by the widely accepted LMCT (ligand to metal charge transfer) process. The 1·Cu(II) could act as an efficient “off–on” fluorescent sensor for homocysteine/cysteine with high sensitivity.
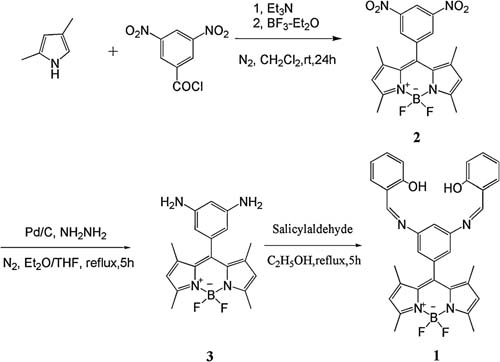 |
| Synthetic route of 1. |
Conclusion: In summary, we have designed and synthesized a new BODIPY based bifunctional fluorescence chemosensor 1 for cations and thiol-containing amino acids. Sensor 1 showed high selectivity and sensitivity toward Cu(II) cations with UV–vis and emission changes based on the LMCT mechanism. More importantly, upon binding of 1 with Cu(II) afforded a non-fluorescent chemosensing ensemble “1·Cu(II)” for the real time detection of Cys/Hcy with high sensitivity and selectivity. Based on the ON–OFF–ON fluorescence of the sensor induced by the Cu(II) cations and thiol-containing amino acids, the sensor has the potential to be employed to design molecular switch.
Published in Sensors and ActuatorsB 171– 172 (2012) 872– 877


