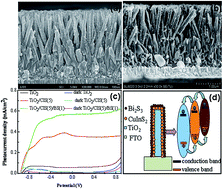
Abstract: TiO2/CuInS2/Bi2S3 core/shell/shell (CSS) nanorods (NRs) electrodes were synthesized by the successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) method and applied as the photoelectrodes for high performance in a photoelectrochemical (PEC) cell, wherein the narrow bandgap non-toxic materials, CuInS2 and Bi2S3, were selected to expand the light absorption range to the near-infrared region. The uniform Bi2S3 layer was directly covered on the previously coated CuInS2 layer on TiO2 NRs to prevent the polysulfide electrolytes' corrosion of CuInS2. The morphology, crystal structure, optical properties and PEC performance of plain TiO2, single TiO2/CuInS2 core/shell (CS) and TiO2/CuInS2/Bi2S3 CSS NRs were investigated in detail. The deposition cycles of CuInS2 and Bi2S3 on TiO2 NRs were optimized to enhance the PEC performance of TiO2/CuInS2/Bi2S3 CSS composites electrodes. The results show that TiO2/CuInS2/Bi2S3 CSS obtained enhanced photoconversion efficiency (6 times higher than that of plain TiO2 and 1.5 times than TiO2/CuInS2 CS). Therefore, the construction of CSS nanostructured composites electrodes through coupling single core/shell nanostructures with another narrow gap semiconductor shell suggests a promising design for improving the absorption efficiency and PEC performance of photoelectrodes.
KeyWords Plus: SENSITIZED SOLAR-CELLS; LIGHT PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITY; WURTZITE CUINS2 NANOCRYSTALS; SEMICONDUCTOR NANOCRYSTALS; NANOTUBE-ARRAYS; NANOWIRE ARRAYS; THIN-FILMS; TIO2; EFFICIENCY; GROWTH
Published in RSC ADVANCES, 5 (96):78902-78909; 10.1039/c5ra14548a 2015


