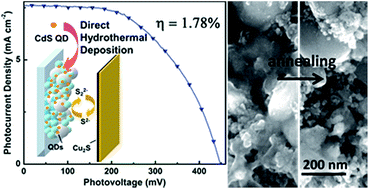
Abstract: A hydrothermal assisted chemical bath deposition method (HACBD) was proposed to directly deposit CdS quantum dots (QDs) on TiO2 photoanodes in quantum dot-sensitized solar cells (QDSCs) for the first time. This method allows a facile and rapid growth and integration between CdS QDs and TiO2 photoanodes, with much lower cost compared to traditional chemical bath deposition (CBD). The post-annealing temperature was found to be crucial for the final performance of the QDSCs. After an appropriate annealing treatment, the conversion efficiency was enhanced from 1.52% to 1.78% under AM 1.5 illumination of 100 mW cm(-2), which is attributed to the red shift of the absorption edge of CdS QDs and lower electron recombination rate at the photoanode/electrolyte interface.
KeyWords Plus: SULFIDE COUNTER ELECTRODES; CDS/CDSE; NANOCRYSTALS; FILM; SEMICONDUCTOR; FABRICATION; NANOTUBES; ARRAYS; CDTE
Published in RSC ADVANCES, 5 (130):107957-107963; 10.1039/c5ra18905e 2015


