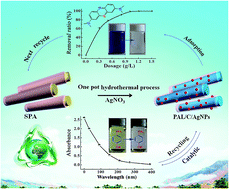
Abstract:Palygorskite (PAL) has been widely used for adsorption removal of dyes from wastewater, but the dyeloaded PAL is usually discharged as solid waste because it is hardly regeneratable by conventional elution processes. As the aim was to efficiently utilize the dye-loaded PAL waste, we employed a facile one-pot hydrothermal process to transform the spent methyl violet (MV)-loaded PAL into multifunctional ternary palygorskite/carbon/Ag nanoparticles (PAL/C/AgNPs) nanocomposites in the assistance of AgNO3. The MV-loaded PAL serves as a carbon precursor, reducer of Ag(I) and supporter of the in situ formed AgNPs. Structure characterizations confirmed that the MV dye was transformed into carbon species, and AgNPs were formed on the PAL with good dispersion, and the addition of Ag(I) ions promoted carbonization of the MV molecules. The as-prepared nanocomposites exhibited excellent adsorption and catalytic performance. Adsorption evaluation showed that the nanocomposite prepared at 5 mass% of AgNO3 dosage gives the best adsorption properties, and 99.2% of methylene blue (MB), 86.9% of MV, 68.7% of chlortetracycline hydrochloride (CTC) and 46.2% of tetracyclines (TC) were rapidly removed from 100 mg L-1 of the aqueous solution using 0.5 g L-1 of the adsorbent. The removal ratio increased with increasing dosage of adsorbent, and the minimum usage amounts of adsorbent for the thorough removal of MB, MV, CTC and TC molecules were 1.0 g L-1, 1.2 g L-1, 3.5 g L-1 and 4.5 g L-1, respectively. Moreover, the nanocomposites could rapidly catalyze the conversion of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) to 4-aminophenol (4-AP) within 6.5 min with a catalytic rate constant of 0.0120 s(-1), and the catalytic activity is still retained after 8 cycles of reuse. In addition, the nanocomposite can be regenerated into new adsorbents by the same hydrothermal process after adsorption of organic matters, which open a new sustainable avenue to efficiently utilize waste dye-loaded PAL and develop new adsorption and catalysis materials.
KeyWords Plus:ENHANCED ADSORPTIVE REMOVAL; SILVER NANOPARTICLES; CATALYTIC-REDUCTION; METHYLENE-BLUE; AQUEOUS-SOLUTION; MAYA-BLUE; HYDROTHERMAL CARBONIZATION; CARBON NANOTUBES; GREEN SYNTHESIS; SEPIOLITE
Published in RSC ADVANCES, 6 (48):41696-41706; 10.1039/c6ra03981b 2016


