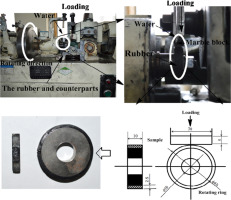
Abstract: As the main component of the tire treads, styrene butadiene rubber (SBR) is widely used to make tire tread for cars in the rubber industry; understanding the friction and wear properties of tire tread rubber is important to improve the safety of the cars. This study aimed to investigate the tribological properties and wear mechanism of SBR under dry and wet conditions; an improved commercial block-on-ring friction testing machine was used to conduct sliding wear tests between SBR and marble block. The friction coefficients, wear rates and wear debris were analyzed under dry and wet conditions in detail. In addition, the contribution of adhesion and hysteresis components to friction coefficient that originated from the changes of loading was discussed. The results indicated that the applied loads have a significant effect on the friction and wear properties of the SBR composites. Under the condition of dry friction, wear losses increased with the increasing load and the main wear mechanism is both severe adhesive and abrasive wear; under the condition of water existence, the applied loads would not affect the wear losses, and the wear mechanism is abrasive wear. The knowledge gained in this study is anticipated to provide the theoretical data for a wear theory study of SBR tire tread and can be used for the optimization of designing higher performance tire treads.
KeyWords Plus: SURFACE MODIFICATION; ABRASION PROPERTIES; MODIFIED SILICA; NITRILE RUBBER; CARBON-BLACKS; FRICTION; SBR; COMPOSITES; FILLERS; BLENDS
Published in WEAR, 356-357 1-8; 10.1016/j.wear.2016.01.025 JUN 15 2016


