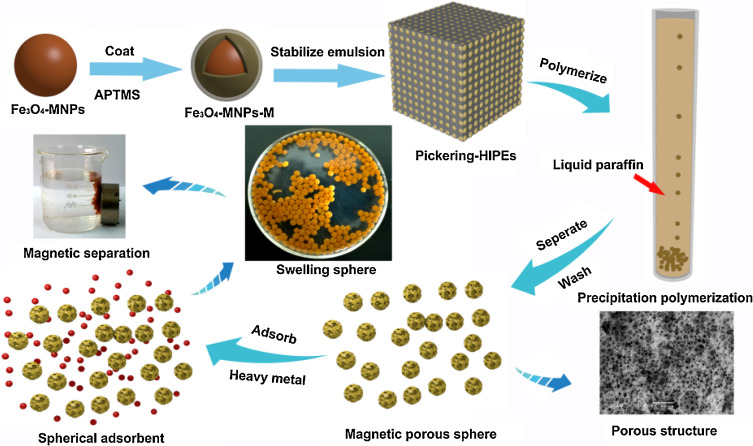
Abstract: A series of magnetic hydroxypropyl cellulose-g-poly(acrylic acid) porous spheres were prepared via O/W Pickering high internal phase emulsions (HIPEs) integrated precipitation polymerization. The structure and composition of modified Fe3O4 and porous structures were characterized by TEM, XRD, TGA and SEM. The results indicated that the silanized Fe3O4 can influence greatly the pore structure of magnetic porous sphere in addition to non -negligible impacts of the proportion of mixed solvent and co-surfactant. The adsorption experiment demonstrated that the adsorption equilibrium can be reached within 40 min and the maximal adsorption capacity was 300.00 mg/g for Cd2+ and 242.72 mg/g for Cu2+, suggesting its fast adsorption kinetics and high adsorption capacity. After five adsorption-desorption cycles, no significant changes in the adsorption capacity were observed, suggesting its excellent reusability. The magnetic porous sphere can be easily separated from the solution and then find its potential as a recyclable material for highly efficient removal of heavy metals.
KeyWords Plus: HEAVY-METAL IONS; POLYMER SUPPORTS; GRAPHENE OXIDE; ADSORPTION; WATER; MICROSPHERES; PERFORMANCE; TEMPLATES; KINETICS; COPPER
Published in CARBOHYDRATE POLYMERS, 149 242-250; 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.04.107 SEP 20 2016


