Abstract: To obtain the valuable p-xylene from biomass with a high selectivity, several transition non-noble metals as main components of catalysts for aromatization of diisobutylene were explored. A volcano curve with the top marked by Cr(3d(5)4s(1)) could be found between the activity and the atomic outer-shell electrons number of transition metals. The further addition of alkaline earth metal showed that the modification of surface properties by Mg doping could improve the catalytic performance. With Cr-Mg-Al-O as catalysts, the enhanced selectivity and single pass yield for the p-xylene formation could be obtained. Meanwhile, the side reaction of cracking could be suppressed, which might be attributed to the increment of the weak/strong acid ratio by Mg addition. Moreover, the catalysts kept a stable catalytic performance in the regeneration and reuse cycles.
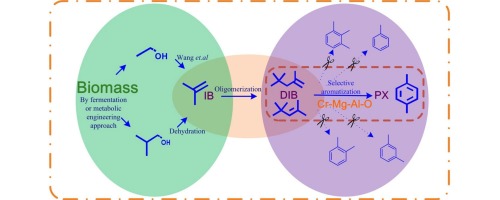
Keywords: p-Xylene; Selective aromatization; Diisobutylene; Biomass
Published in CATALYSIS TODAY, 276 105-111; SI 10.1016/j.cattod.2016.01.054 NOV 1 2016


