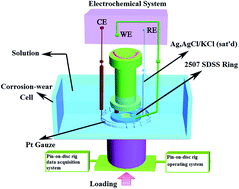
Abstract: Wear-corrosion behavior of SAF 2507 super duplex stainless steel (SDSS) in different concentrations of NaCl (from 0.5% to 8%, w/v) was investigated using a pin-on-disk tester. Friction coefficient and mass loss rate were determined, and the synergistic effect of wear and corrosion was analyzed by tribocorrosion-related parameters. It was indicated that wear-corrosion regimes were significantly influenced by NaCl concentration and the related mechanism was attributed to the two different phases inside SAF 2507. Self-protection behavior between the two phases inside SAF 2507 led to a significantly different wear-corrosion mechanism, compared to that in the single-phase metal. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study about wear-corrosion behavior of SAF 5207 within a solution with different corrosivity. This research provided a new insight for researchers to look into the tribocorrosion behavior of alloys with different phases, and helped us to better understand the principle that we should follow while developing alloys employed in a corrosive environment.
KeyWords Plus: ARTIFICIAL SEAWATER; AQUEOUS SLURRIES; CHLORIDE-ION; ALLOY; TRIBOCORROSION; 304-STAINLESS-STEEL; ENVIRONMENTS; RESISTANCE; 304SS; TEMPERATURE
Published in RSC ADVANCES, 6 (112):111261-111268; 10.1039/c6ra23030j 2016


